Hello to everyone ?,
I am back again with the guideline how to do or what is. I am getting lot of questions from my about how to create an effective marketing plan.
First and foremost lets precise the difference between the marketing plan and marketing strategy. WHY? Because these things have differences and each fulfill another and many clients get lost in these terms once they are not experts in marketing.
So marketing plan is a tool to meet the goals of the marketing strategy. With this being said the marketing strategy is superior to marketing plan.
Few paragraphs later I will explain more in detail the slight differences but this is the short answer what is the main difference, therefore you could have a grasp what is going on and not to be lost in terms.
Well marketing plan (owned by marketing manager) is a roadmap (support document) to meet marketing strategy goals or execute the strategy. YES, the marketing plan has parts such as strategy and tactics but these parts tell us how to meet the objectives of the marketing strategy.

On the other hand the marketing strategy is a strategic document (usually owned by CMO), that supports main business goals of the company. Contains high level elements about competitors, products, brand etc.
Yep therefore once we are creating the marketing plan we use the marketing strategy as our guideline to be in line with company goals. Once said, marketing is what, why, when and how. The marketing strategy is our “WHY and WHAT” and the marketing plan says “HOW and WHEN”.
Hm, need more methanphore ? ? So, the marketing strategy is our ship and marketing plan is wind to move our ship into the specific harbour (objective).
Well, now once we are clear about these differences it is time to say that is article or guideline will be about the marketing plan ?. It was very important to tell you about this difference because during the marketing plan article I will refer to some part of marketing strategy and vice versa.
No worries I will definitely write an article and ebook about the marketing strategy ?. Well enough of self-promotion and let’s deep dive into the marketing plan.

What will be the key takeaways of this marketing plan article? You will learn:
- Why you need a marketing plan?
- How to write a marketing plan
- Marketing Plan – Executive Summary
- Situation Analysis
- Marketing Plan Objectives
- Target Audience
- Industry & Market Analysis
- Brand
- Positioning & USP
- Media strategy & Tactics
- Marketing Budget
- Objectives & KPIs
- Few Hints
Downloadables
What is the difference between a Marketing Plan and Marketing Strategy?
As I mentioned hereinbefore lets take a closer look to the difference.
Marketing Strategy
Shaped by your business strategy, your marketing strategy is your purpose; it’s the offering you deliver, WHY (the reason) you will deliver it and WHAT (the product) your marketing efforts deliver in order to achieve your company’s mission and strategic goals.
While many people think about jumping into action when it comes to marketing, having a clearly defined marketing strategy is incredibly important for your business growth. Guys and I am serious about it. Once you do not know the strategy the outcome from the marketing plan will be mediocre, coincidental and disappointing for you.
On top of that you will deplete lot of your money from your marketing budget without a quality result. Trust me that marketing strategy is your backbone of all your activity if you are serious about your business.
Many entrepreneurs come to me for help, that they spent most of their budgets without significant result. My first question is, “What is your marketing plan”, well mostly they do not even know what is it. So please do your objectives and marketing strategy first.
Once you have your strategy or at least objectives what you want to achieve, only then will you be able to develop an effective marketing plan.
Marketing Plan
Driven by your strategy, your marketing plan is the execution; the roadmap of tactical marketing efforts that help you achieve your marketing goals. Your plan is your detailed campaign of what you will do, where you will do it, when you will implement, and how you will track success. It is your “How and When” of your marketing answers.
You’re posting on social media, you have blog posts but you’re not seeing any results. What’s the deal?
The problem isn’t what you’re doing, it’s why you’re doing it. If your marketing efforts are not backed up by a strategy then that’s probably why you’re not seeing results.
Before posting a content, you should always start with your marketing strategy and then use it to support your marketing plan and efforts.

Why You Need a Marketing Plan
As much as you want to keep procrastinating, a marketing plan is a must for your business. Here are ten truths that will motivate you to put some structure around your business growth asap.

1. It forces you to think
The act of physically composing your marketing plan forces you to formulate and articulate your thinking about your customers, your product, and how you bring those two things together. Explicitly thinking about these things is important. Talking about them with the other members of your team, particularly the team members who will be carrying out the plan, is crucial.
2. Setting measurable goals

Far too often, small businesses settle for “sell more next year than last year” and “don’t go broke” as metrics for gauging their success.
Measurable goals create tangible targets for you and your people to work towards. Tangible targets increase performance far more than nebulous “just don’t fail” hopes.
What I mean by measurable goals? Number of leads, email subscriptions, audience reach, orders put through the shopping cart, post views or new customers.

3. Motivation for an organization
The human brain is outstanding at taking purely arbitrary goals and making them super important. This can be problematic, but it can also work for you. People will literally go the extra mile to get that last sale if “Make ten sales a week” is their goal, because the pleasure we get from achieving the goal makes it worth it—even when we set the goal ourselves.
4. A plan helps you organize your time and priorities
Extremely important. Once you start running your business leads are more important to you than let’s say email subscriptions and even more important is to choose the right objective and marketing channel to reach your goals.

5. It will earn you money
If you’re going to be going to investors at some point in the immediate or near future, then you’re going to have to have a marketing plan in any event. You might as well start working on it now, so that the plan you actually present to your venture capitalists has actually been hammered on in the forge of experience. They’ll be able to tell, and that will make a difference.
6. Wise budget – money spending
Like your time, your marketing budget is finite. It is important to spend your budget to most effective channels for your business. To get value for money from your marketing activities.
Marketing should bring back your invested money and increase your sales otherwise is something wrong in your plan.
7. You will be proactive and not reactive

Reactivity is a besetting problem for small businesses, because we often simply don’t have the resources to anticipate everything days or weeks in advance. That can be a strength, because small business tends to be very flexible and able to handle shifting conditions quickly, but it also makes carrying out a disciplined course of action more difficult.
Having a written plan gives you the ability to know what your reaction to things ought to be *in advance*, which lets you preposition your response when you see things coming.
8. It provides reality check
Reality check between your objectives and your marketing strategy.
9. You ‘ll provide better customer service
When you know what your marketing plan is, that means you know how you want to serve your customers.
It’s almost impossible to do a good job of something that you’re uncertain of how to do; only when you have a target in mind does hitting that target become more than a matter of pure luck.
How to write a marketing plan
Good marketing plan uses tools and tactics to achieve desired goals. Marketing plan is activity planning in time – What we are going to sell, when, how and to who (WHAT, WHO, WHEN and HOW)
Now is the right time to use our HOW and WHEN.
Before we start with creation of the marketing plan I recommend to use one methodology named SOSTAC, this methodology is used for planning.
Situation – Where we are.
Objectives – Where we want to be.
Strategy – How we gonna get there.
Tactics – How exactly we get there.
Action – What is our time plan.
Control – Are we there? Verification based on KPIs.
Well below is the better overview how to shape your marketing plan so let’s dive in.
1. Maketing Plan – Executive Summary
Every business needs a smart marketing plan to attract money and investors. Without the right cash flow, the business and its owners are under constant stress. I talked a lot about the executive summary in my previous business plan article.
The executive summary is a synopsis for the reader (investor, CEO) or anybody that will shortly tell the most important points of your plan. For the marketing plan purpose I would say for any interested party as CMO, marketing staff etc.
A mini version of your plan
The executive summary is a mini version of your marketing plan – an elevator pitch. It has a section that summarizes each component that your marketing plan covers in detail.
Keep the executive summary to less than one and a half page. There is no set guideline for how long the summary should be, and it often reflects, to some degree, the length of your entire proposal.
Keep in mind that a marketing plan can be anywhere from four to 40 pages or more (bigger projects or yearly marketing plans). Yep, but best practice is not to have too long marketing plans as you will lose attention of the reader.
Keep it short and be to the point. The executive summary should concisely highlight the most important information. For each section, think about summarizing with one question in mind: Why is this information important to the success of my business?
Key components of the Executive Summary
he Executive summary contains subsections that correspond with the marketing plan subsections. These may include:
- What does business do?
- What market you need to serve and shortly about the market?
- What are your objectives?
- Major Problems which you wants to focus on?
- Your Product which helps in removing that problem.
- Buyer persona or target audience definition.
- Positioning of your product/ service.
- Strategies and tactics/ channels to be used
- Budget you are going to need
With only a few sentences to summarize each section of the actual plan, make sure you are thinking in terms of sales and marketing when writing it. Please be concise and do not exceed more than 1-2 pages at maximum otherwise you are going to lose reader’s attention.
2. Situation Analysis
The situational analysis section is one of the most important parts of a marketing plan.
Well situation analysis briefly describes following aspects:
- Markets you compete [local, national, global?] – Size of the market, your market share and competitors’ market share.
- SWOT analysis (For more info refer to my previous business plan article).
- Marketing communication of your competition.
- Definition of the product lifecycle its seasonality and time behaviour differences.
- Your vision and mission
Situation analysis describes your WHAT and WHY of your company, this part comes from marketing strategy. You describe the product most of the time very shortly just to introduce the reader into the problematics.
Short history and location to have better understanding when using certain strategies and tactics. Vision and mission is the must as you should maintain and complete the main attributes of your company.
3. Marketing Objectives
Marketing objectives are goals set by a business when promoting its products or services to potential consumers that should be achieved within a given time frame. In other words, marketing objectives are the marketing strategy set in order to achieve the overall organizational objectives.
A company’s marketing objectives might include Brand Awareness, New Product Launch, Lead Generation, Engagement, Nurturing etc.
Briefly, if you do not have marketing strategy you should have at least your objectives. Maybe I should not say (write ?) the following but you can temporary or somehow create your very simple marketing strategy in your marketing plan.
I have to bold and underline the word temporary as marketing strategy is must have.
Below are 5 key objectives any brand should integrate into their social media strategies.
A. Brand Awareness
Creating brand awareness shortens the sales process, increases market share, and positions a brand as a leader in its sector.

Well that’s far more ways how brand awareness can help you and one of that way is strong position during the negotiation.
Brand differentiation can develop from a number of actions such as the creation of original content, personalized promotions aimed at the target audience, prospect profiling, product development based on social insights, and communication strategies adapted for socio-demographics of interest.
Here are some KPIs to help you track and report on the success of this objective:
- Mentions: the number of times the brand comes up in social media conversation and the number of times these conversations are shared.
- Impressions: the number of potential views that a message has. In the online environment you can see keywords as your brand, well that’s the point of quite strong awareness.
- Reach: the number of people who have received viewed a publication.
- Social Sessions: the number of site visits, blog post views, etc.
- Share of Voice: volume of mentions received by a brand versus volume of mentions received by all relevant competing brands.
In the nutshell, the objective for awareness are often more general such as reach, impressions or mentions.
B. Lead Generation
Lead generation is the process of capturing the interest. Well by leads we mean business opportunities that come to you and sales should turn these opportunities into customers.
When measuring lead generation in your marketing plan you as a lead generation you can define whatever goal:
- Prospects interested in your product.
- Filled contact forms for your product/ service.
- Email subscriptions for your service/ product.
- Free trial or freemiums of your product.
Well simply said, everyone or every action made that can produce a potential customer.
C. Engagement
This objective is the use of strategic, resourceful content to engage people and create meaningful interactions over time but not only content also an activity.
With today’s connected and overwhelmed consumer base, people are seeing about 3,000 messages a day—out of which a person will remember an average of four and guess what, mostly those messages with better brand awareness, also creativity here plays crucial role.
Bear in mind that people hate to be sold everytime you can. Creativity plays crucial role in the engagement. You have to create a message, action or activity to which people start to respond.
Yep, you need to have buyer personas for that, thus you could create exactly what your target audience needs.
Some engagement examples:
- Content type: Likes, reposts, shares, comments or similar.
- Reviews for your product often when customers are delighted by your product/ service.
- Time on site, video that visitors spend by watching.
- Word of mouth, well similar to reviews, but once customers or people are delighted they will tell about their experience to others.
- Participations atyourevents, activities etc.

D. Lead Nurturing
Or simply said creation of a relation with your leads (prospects). There are many ways how to do it. Mostly it is often done by emails, warm calls or sales reps to check whether potential customer may need or regular blog posts etc.
E. Traffic
The Traffic objective is designed to drive people to your website, app or even to your brick&mortar. With Traffic as your objective, you can create ads that:
- Send people to a destination such as a shop, website, app or Messenger conversation (website clicks, shop visits).
- Increase the number of people going to your mobile or desktop app (App Engagement).
F. Conversion
A conversion in marketing is when a visitor to your website completes a desired goal.
In this way, they convert from visitors to leads or, if they purchase something, to customers. A conversion occurs when someone changes from a passive visitor to an active, interested visitor or customer. Well we all want to measure this goal as this is often considered as the customer action or desired action.
Conversion examples:
- Sales
- Downloads
- Email subscriptions
- Time spent on page
- Items in the basket etc.
Now, you should have a good grasp about your marketing objectives. Hey! Why I started with the objectives?
Because, not even in the marketing but also in your life or any action you are going to do. Please, before doing anything, think little bit of what are you going to/ want to achieve by doing certain activity.
Starting any activity in marketing without setting the objectives or goals is waste of your time, money and energy. All the results will be just a coincidence ?. Even in the life, when doing anything without thinking, you can not have desired result.
Creating a Marketing Plan
A good marketing plan spells out all the tools and tactics you’ll use to achieve your sales goals. It’s your plan of action — what you’ll sell, who’ll want to buy it and the tactics you’ll use to generate leads that result in sales.
It is right time to our HOW and WHEN what are exact questions that marketing plan responds to. Here’s a closer look at creating a marketing plan that works.
4. Target Audience (Buyer Personas)
Simply put, your target audience is the group of people you’re making your products and services for. Other terms used to describe this group are “target market” and “target customer” OR very common “buyer personas”. This part is extremely important as you need to known your focus.
Step1: How to Identify Your Target Audience
Now that you know why a target audience is essential, it’s time to select your first audience group. Below are a list of characteristics you should consider identifying (use the attached worksheet for guidance):
Quantitative Characteristics
A. Demographics ???
Demographics are the criteria you use to describe a specific part of the population. Some example of demographics include:
- Age
- Gender
- Income
- Marital Status
- Occupation/Industry
- Educational Level
B. Location ?
You can also narrow down your audience based on geography or location. You can pick a neighbourhood, city, province/state, or country. You can also specify via distance. For example, you can target customers within a 10-mile radius of your city. Or you can target customers within your city and the cities that surround it.
C. Psychographics ?
Unlike demographics, a group’s psychographics are more difficult to guess externally, since these are more relevant to their personality. Here are some audience psychographics you can specify:
Interests/ Activities
These could include topics of interest, hobbies, regular activities, and behaviors. Some examples:
- Board game enthusiasts
- Frequent backpackers
- Beginning gardeners
- Stamp collectors

Qualitative Characteristics
Better describes deeper intentions of your buyer personas. This are mainly topics like pains, needs, struggles, targets of your buyer persona, aspirations, marketing message or elevator pitch.
Based on the qualitative parameters you will be able to build your message house for each persona he/ she will respond to later.
How to get target audience data?
In this case you do an interview with a sample of your target audience. Moderated interview with length of 40-50 minutes will uncover all necessary details you need to complete your target audience definition.
If you need a faster way of getting the qualitative data, I recommend to ask an expert with years of experience in a given domain.
Step2: Useful Marketing Tools to Identify Buyer Personas
Even after following the steps above and filling out the worksheet, you might not feel sure about your selected audience. If you need help figuring out your target audience and learning more about them, the following tools can be useful

1. Facebook Audience Insights ?
Facebook Audience Insights is a tool that can help you specify and learn more about your target audience. You start by selecting different audience criteria such as location, age, interests, and behaviours. These insights tell you what kind of audience are your visitors and then you can better tailor your strategy.
You can use this tool also vice versa so when creating facebook marketing campaign you select precisely to who target with your ads.

2. Google Trends ?
Google Trends helps you determine interest in a particular keyword or topic over time. This can be helpful if you want to narrow down a location for your business idea, as well as any general trends.
3. Google Analytics ?
Item Audience will tell you a lot about your customers. What kind of technology they use, more mobiles or desktops? What channels they use, what kind of behavior.
Well there are so much other marketing tools to define your audience. But these three mentioned above are sufficient to create your first draft of buyer persona. Once you pre-define your audience based on insights it is time to create few questions with multiple choice answers to finalize your quantitative research.
I prefer to prepare exact matrix of questions up to 10-13 that fill each other and if you combine them you will get answers on many other questions. I usually do internet questionaires on new customers or existing ones (google forms are also fine).
Well quantitative research can be done also by other way. If you are a specialist in a given domain or you know any specialist with years of experience in that domain you can talk to him and he will give you valuable output about your buyer personas.
If you are running on higher budgets i recommend to use internet questionnaire for 100% quality of the output. Qualitative research can be done again with the specialist with years of experience in the given domain or by interviews of your buyer personas in the dialogue.
5. Industry & Market Analysis
How to do a market analysis?
The objectives of the market analysis section of a business plan are to show to investors that:
- You know your market
- The market is large enough to build a sustainable business
In order to do that I recommend the following plan:
Business situation [Lifecycle – mature? Grow? Decline?]
Life cycle models are not just a phenomenon of the life sciences.
- Even within the same industry, various firms may be at different life cycle stages. A firms strategic plan is likely to be greatly influenced by the stage in the life cycle at which the firm finds itself.
- So its very much important for nay business to find out that in which lifecycle their business are in.
Market size, saturation, market share CAGR [statistics] of the target market
- Market size in terms of money. Then you can also define your market share (%) and penetration.
- This is an aspect that many startup founders in the innovation community tend to overlook, since they get excited about the product they’ve developed without thinking about how it benefits their audience.
- CAGR (%) tells you how your market potentially will grow during next years. Maturity markets have minimal or 0 CAGR if not negative one.
Problems, drivers, challenges and threats on the market (Very important)
Understand the various types of problems in your business and make a Marketing plan on how you can solve those problems.
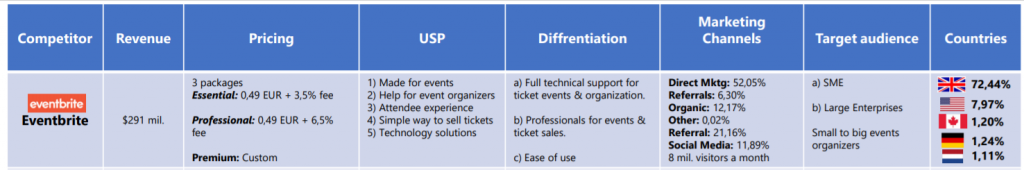
Competitor analysis and their profile
- The Competitive Analysis section of your business plan is devoted to analyzing your competition–both your current competition and potential competitors who might enter your market.
- Every business has competition. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of your competition–or potential competition–is critical to making sure your business survives and grows..
- In fact, small businesses can be especially vulnerable to competition, especially when new companies enter a marketplace.
Well at the end of the market/ industry analysis I have to say that this is open category. You do your analysis according to your needs you want to define. You can measure market penetration, marketing spending of your rivals, services offered etc.
What to analyze?
- Market share
- Differentiation and positioning.
- Unique selling proposition of your competitors.
- Used marketing channels (SOV – Share of voice, traffic).
- Marketing budget of your competitors and budget for marketing channels.
- Competitor size & revenue.
- Sample of communication message.
6. Brand
When it comes to having a brand strategy, it’s not enough to simply have a few bullet points of what you want to do. Brands today need both a thorough understanding of why they choose certain strategies and a detailed outline of what their strategies will be.
Why? Because the more detailed you are in your branding strategy, the easier it will be to succeed when you execute those strategies. Brand or brand strategy is defined in your marketing strategy. It is mostly what brands stand for, what values represent it, identity, image and characteristics.
Here are main three things every brand needs to define:
- Identity ➡️ What represents your brand, what stands for, reason to believe
(Apple ➡️ Success and style, Nike ➡️ sport, freedom, goals achieving) - Brand values ➡️ Can be emotion or performance.
- Brand characteristics ➡️ Quality, luxury, success, personality.
These points should be defined in your corporate marketing strategy. Knowing the answers to each question will help determine what your goals should be, how you should approach your customers and how you’ll measure your success in meeting your goals.
Following are the 3 aspects one should keep in their mind before making a Marketing Plan for their business:
- Positioning (Point of Difference)
- Unique selling proposition of their business
- Defining the voice of the brand for their business (This is just tone of voice you are using in communication with your customer – familiar, friendly, corporate or other).
We will pass through these points in next chapter Positioning.
7. Positioning & Unique Selling Proposition (USP)
I think in business plan we talked about these two features such as positioning and unique selling proposition. Well by few sentences I explain the difference again.
Positioning (often also referred as point of difference or differentiation) ➡️ is how you position your product/ service on the market in the eyes of your customer. Usually you choose 1 – 3 strong points that are demanded by your target audience (from previous buyer persona analysis) and you build your product/ service or brand around these differentiations.
Broader definition of positioning here. Here is also good longer definition of positioning.
Unique selling proposition (USP, also referred as unique selling point) ➡️ Well this is quite different to positioning but similar ? Confused?
No, you should not be. USP are simply said benefits for customer.
It can be highly innovative product, super customer support 24/7 (Zapos build brand on this), well it can be also lifetime warranty or others. USP definition. Some good USP examples HERE.
Well now, when you definitely know the differences how to implement it into your marketing plan? Usually use only one slide max per each, just to keep in mind during all activities and campaigns your key differences and benefits to customer that you promote.
According to USP and Point of difference you build your messages sent to customers. It can be text on billboards, paid Google ads or Facebook ads.
How to Create Appropriate Positioning
Before creating a proper positioning you should know basic elements about your target audience and brand. Positioning is mentioned in your corporate marketing strategy. This is just a quick shortcut how to create positioning.
- Know the needs of your target audience.
- Tell who you are to your target audience.
- Show to your buyer personas how you can satisfy their needs.
- Differentiate from competitors. Define 2-3 attributes that make you standing out of the crowd.
- The most important part for the marketing plan is to insert your point of difference into your key messages.
Again USP part is defined in your corporate marketing strategy. So I only mention its creation in brief. You have to communicate the benefit for the client. Where you should know what needs the customer? In your target audience part. It is important to describe our solution in language of the customer.
For our purposes let’s say that we are sellers of sport equipment, especially running shoes.
USP Template Formula
- WHO (For which type of the buyer persona? – Runners)
- Need (For those who need quality running shoes)
- What (Product)
- From WHO (Seller/ Producer of the given product)
- Solution (Performance improvement, traction on the race surface)
- Point of difference (How to differentiate from the competition – “Verified seller by years and official partner of the Olympic running team.”)
I recommend to point out several benefits for the client.
- Quality running shoes
- Known seller with years of experience and results
- Shoes improving your running performance
- Professional seller/ producer (Guarantee of quality). To increase attraction of our USP I recommend to use several years warranty in case it is possible.
USP in practice (Google Ads)

Below I add several USP from well known brands.
The Economist
“You have seen the news, why not to discover the story.”
Other news media just write or talk about the news. The Economist goes beyond and offer the story behind the news.
Tiffany & Co.
I think that all of us heard the story about the pin for $999. Yes that’s exactly Tiffany & Co. brand.
When selling the weeding rings they used very interesting message to demonstrate their USP.
“The right one is worth waiting for.” They defined WHAT, for WHO, PRICE and QUALITY.
AirBnB
Another known brand. The USP for AirBnB is as follows: „Book unique places to stay and things to do.“ Simple summary of all benefits for the client.
USP mentioned hereinbefore are one phrase type. You can use the manner above or define it more simple in phrases or bullet point on the website. It is important to clearly define the client’s benefit.
8. Media Strategy & Tactics
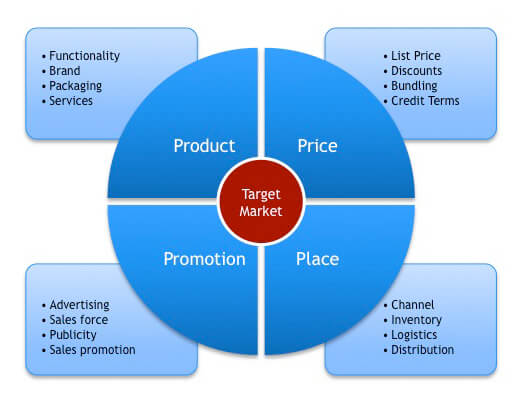
Fine this chapter is important, but should be defined in your marketing strategy. This is what your whole marketing plan is all about. What kind of channels are you going to use, what is their mix and individual tactics for each channel. Well somebody may ask me: “Hey wait, what about the marketing mix of 4Ps?”
Good question and I will answer it right now. Your marketing mix should be mentioned in your marketing strategy but I define few elements of it.
Product – P
Packaging, services, brand should be defined in marketing strategy. In case there is a specific packaging prepared for certain marketing campaigns let’s say with celebrity you can define this packaging in your marketing plan.
Price – P
Similar to product issue, pricing policy is defined in your marketing strategy. You can use different pricing policy for special marketing campaigns like those of countdown or special season offer.
Place – P
I stop here for a while. It is known that marketing is about good location and it is very important factor. It is same for digital campaigns that you want to place your ads to website with high traffic.
Promotion – P
This part talks for itself. This chapter is dedicated to right promo setup. We can say that the marketing plan is extended hand of the marketing strategy.
I would breakdown this part into smaller paragraphs to make it more obvious.
- Main goals to achieve
- Media mix – (online, offline)
- Marketing Funnel definition – Main pillars
- Marketing channels – strategy , detail description
- Media plan – tactics
- Creating a content calendar
8.1. Main Goals
Here is the summary and definition of goals you want to achieve by your marketing campaign. Do remember that these goals are broader ones. In the chapter KPIs and measures we will dig deeper in how to measure these goals. Let’s say you can have 2 main goals. According to these goals you set up your marketing channels and media mix.
- Awareness ➡️ Getting into the mind of your customers.
- Lead generation ➡️ Generate some leads that will be later turned into customers.
Well goals can be any you prepare and want to achieve but do not overwhelm your self with too many goals.
For purposes of this marketing plan let’s use these 3 goals and we will create strategy & tactics to achieve them.
8.2. Media/ Channel Mix
Short description of planned media to use to achieve your goals. Very short description, pls see the picture. You can put main goals and media mix into one slide/ page if appropriate.
8.3. Main Pillars – Marketing Funnel
Well I tell you something about 2 models that are most used (they are similar) so you can choose one of them.
The AIDA Model, which stands for Attention, Interest, Desire, and Action model, is an advertising effect model that identifies the stages that an individual goes through during the process of purchasing a product or service.
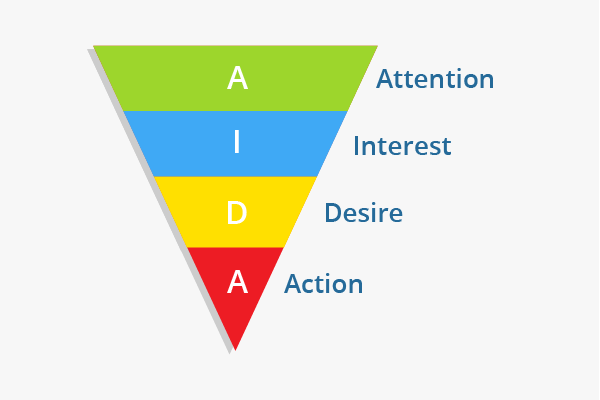
The AIDA Model Hierarchy for Target Market Identification
The steps involved in an AIDA model are
Attention: The first step in marketing or advertising is to consider how to attract the attention of consumers. Well most demonstrated examples are on sneakers, so lets repeat it. User likes running and he will check all blogs and information on the internet or elsewhere about running and how to increase running performance.
What you can do? You can write a running blog on how to improve your running habits or performance. And do not forget to say that Iont drinks, proteins or running shoes increase his/ her running performance.
You are pre-warming your future client.
Interest: Once the consumer is aware that the product or service exists, the business must work on increasing the potential customer’s interest level.
What you can do? Now your user lets say potential buyer or buyer persona now, knows few hints about running and knows what improve his/ her performance. Knows that iont drinks exist with super duper proteins and dope running shoes.
Now consumer check brands offering running shoes, proteins or iont drinks and check their specifications what they do. Well he/ she is interested and takes the running more seriously.
So consumer is checking testimonials, PR articles about how to increase your running performance, product benefits. User is susceptible to influencers, video blogs, reviews or PR articles in press/ digital press.
Desire: After the consumer is interested in the product or service, then the goal is to make consumers desire it, moving their mindset from “I like it” to “I want it.”
What you can do? Now we are in the head of the consumer your potential client and he is switching to Yeah I need those iont drinks, running shoes and proteins to run my 100 metres below 12 seconds.
But which ones are best for me? Well future customer check deeply price of the products, reviews from influencers, existing clients, selecting the best product for him. Paid search or emailing is now very suitable for him/ her.
Action: Your user/ buyer persona is ready to go, to buy from your website so in this phase you use many call to actions or ads with direct words like buy now, discounts for volume purchase or free shipping. Your user want to buy the product and he is considering where to buy it.
It is time to use your arsenal of discounts, paid search, bulk discounts, warranties, crazy call to actions ?.
Well the second model is very similar and my favourite, it is called See, think, do care. Lets say compared to AIDA ➡️ See has two AIDA phases awareness and interest, Think is the phase of desire and do is the phase of action. Well what about the CARE phase?
This phase is after sales phase that customer wants to prove yourself that he/ she made a good purchase. Well customer care or support comes at place, emailing for complementary products, inclusion into fan page or FAQ forum.
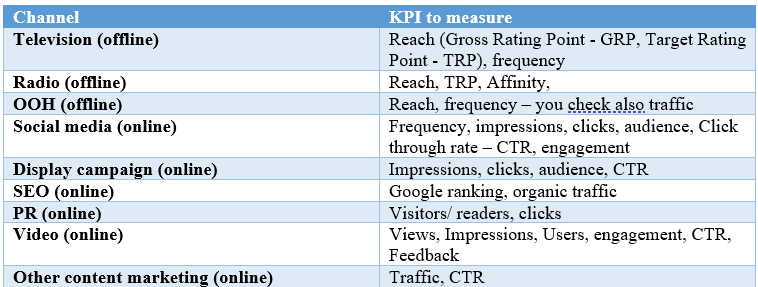
8.4. Marketing Channels
In this section we define channels for each goal we want to achieve. In your marketing plan you usually write down little bit about the channel and process of usage of this channel.
Choose the channels from your media mix. I will write about 1-2 channels for each marketing goal as you can have a grasp of how use it and define it. Well I take into account that the goals of this article is the marketing plan creation and not the guide through the marketing channels and tools ?.
Marketing channels for Brand Awareness
I. OOH Advertising (offline channel)
Out of home or outdoor advertising, well known by everyone. In other words billboards, megaboards, city lights etc… You should include Time of support.
That means how long this campaign should time thus starting and ending date, budget used for this channel, price for this channel during whole period.
Expected outcome
Thus what traffic will pass around these billboards, count of impressions or hits and frequency. Additionally I recommend to show some examples from campaign, places where the billboards will stay.

Guys this article have nothing with McDonald I use it only for illustration to show you how it should look like ?.
II. Paid Advertising (online channel)
Another perfect tool for brand awareness is paid advertising (social media not included , that’s another channel). Let’s include only Google Ads (YouTube excluded it is social and for video formats) or other PPC systems. In Slovakia it is used also eTarget.
For awareness purposes you can include search campaign and display/ banner campaign.
Display/ banner campaign in Google Ads
It is often focused on websites with high volume of traffic. You set up your Timing (ex. 09.01. – 24.11/2020), budgetyou want to use and also you should know the number of impressions and clicks in advance. (Google and other paid systems are able to define these metrics in advance).

Well there are many channels out there that are suitable for branding campaign but this article is about to set correctly your marketing plan and not to define suitable channels for marketing campaigns, that is a different story. Well I just mention you most common channels for brand awareness purposes.
Marketing channels for Lead Generation
Well lead generation objective is a different story. You can use very similar channels than for brand awareness but in a different way with different messages.
For lead generation you try to take something from the customer, like the goal can be subscription, email, phone number or any other attribute that will be later used for other actions.
I have to say according to your business you choose most suitable channel for your lead generation and whole communication.
- Cold Calling (offline)
Well this is one well known method of generating leads. I think that majority of us or all of us have received calls from stock exchange experts etc. Focusing on lead generation via cold calling can be done by the support of quality call center. On the other hand you can define specific objectives to reach your lead generation goal.
Objectives:
- Sending email with a service information
- Generate a meeting with an expert from the given company
- Subscription for specific newsletter
- GDPR consent to send regular updates and offers.
II. Search Engine Optimisation – SEO (online)
Online way for the lead generation. Again as I said previously this channel can be used also for direct sales it is up to you what kind of an objective you are after and which way you use it. For SEO campaign you define timing, budget and specific keywords you want to target.
Afterwards you set up your KPIs such as organic visits and keyword ranking.
8.5. Marketing Campaign Timeline
Well once you defined your goals, channels it is time to set up timing to your marketing campaign. For the timeline you put all channels and activities into one chart, I prefer Gantt diagram, where you can see timings of all your campaigns.
This chart is very important and its usage is really handy during the whole year.
8.6. Content Calendar
This paragraph is little bit off records, but I just want to notice that same as you have a timeline for marketing activities, you should create your content calendar that will define a content for every month or week you want to publish.
This must be aligned with your marketing activities.
9. Budget
Marketing budget keeps your entire team focused on specific goals – it’s a critical resource for your goals. It takes time to develop a good marketing budget, but it’s important because it ties all of your activities to tangible goals.
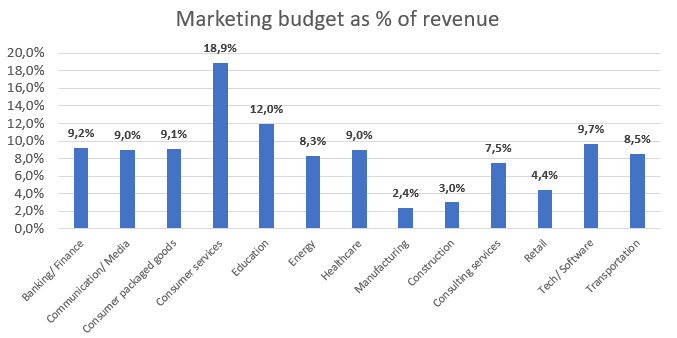
Marketing Budgets per Industry
Very common question comes in to a place that How big should be your marketing budget? Well it depends on your goals and phase you are at.
You can have conservative budget to keep your position or the budget increasing your market share and penetration or even very fierce budget that is used for expansion to new markets. It depends also on industry and competition. There are industries where marketing budgets are very high mainly industries where your success and revenue depend primary on your marketing expenses.
Rule of thumb
Marketing budgets generally hover between 6 – 11% of total revenue. B2C segment uses 15.6% of revenue. B2C segment uses 8.6% of revenue. According to industry the marketing budgets are as follows:
How to setup your marketing plan budget
Well according to the information hereinabove you should be now comfortable with setting your budget.
On the other hand I add below few methodologies (from finance) how to setup your marketing budget. This is just an advice and you do not have to go by it, but it helps once preparing your budget.
Activity based budgeting (ABB)
This type of budgeting is based on your all marketing activities that occur during the year. This is why you have to have prepared marketing plan timeline as you can correctly setup your budget.
I recommend to use also a buffer as 5-10% of your total marketing budget for any unplanned activity or spending that may occur.
Zero based budgeting (ZBB)
Often used method, quite time consuming but very precise. You built your budget from scratch and you have to take into account each activity you are going to make. Similar to ABB method but ZBB method is more tight and precise.
Value proposition budgeting (VPB)
This type of budgeting is considering the following aspects.
- A reason why is given amount included in the budget.
- What added value will have any marketing activity. Is it worth of money?
- Does this activity will give us positive ROI (Return on investment)?
There are also other budgeting methods but these are most common ones. After this budgeting chapter you should have quite good grasp of how to prepare the budget for your marketing plan. Let’s dive into next chapter, objective setting and measuring.
10. Objectives & KPIs
Successful goal setting requires placing KPIs and benchmarks on your plans. You need to assign numbers, deadlines, and metrics to each of your marketing objectives.
Because what you can not measure you can not improve. All results will be then a coincidence.
KPIs and marketing metrics allow you to evaluate progress along the way and assess results at the end of your campaign. Without benchmarks for your goals, you will have no way of knowing whether your work was successful or not.
When choosing a KPI, you are essentially homing in on the Measurable component of the SMART rule, asking yourself which metrics will let you determine whether or not an effort has been successful. KPIs, like your social media goals and objectives, should be based on what your team can actually do to influence the achievement of the Objective. That is, KPIs should only measure things that you and your team have direct control over.
Once you’ve established a KPI by choosing relevant metrics, you’ll need to settle on a target number that’s achievable, yet ambitious.
The best method for determining future targets is to establish benchmarks. You can do this by extrapolating data from past efforts to estimate future success. For example, if you’re partnering with a YouTube influencer, look at the view counts of their past videos and base your KPI target on that data.
How to measure the success or failure of marketing campaigns
Here are five metrics to help give a more in-depth insight into the effectiveness of your marketing efforts. Well let’s go one by one. As mentioned before we are after two types of campaigns brand awareness and lead generation. You can focus on many more goals but for the purposes of this marketing plan let’s choose few.

Brand Awareness
Goal: Improve your brand perception and affinity, let know about your brand and industry you operate.
KPIs & Metrics ?
- Impressions (how many times was seen your ad)
- Reach (how broad audience was reached by your ads, similar to impressions)
- Frequency (how often a single person have seen your ad, 1.6 or 3 times etc.)
- Website traffic (how many visits have you reached from your ads)
- Engagement (shares, likes, follows etc…)
- Brand mentions (how often is your brand mentioned)
Lead Generation
Goal: Incite any desired action. Produce more potential customers (prospects).
KPIs & Metrics ?
- Subscriptions
- Newsletter subscriptions
- Given contacts
- CTR ➡️ Click through rate
- Conversion rate (this is also sales metric)
- CPA (Cost per action) or CPL (Cost per lead)
- ROI (Return on investment – also sales metric)
Few Hints
Well we are approaching to the end of this marketing plan guide. Below I give you few marketing plan tips that will help you to fine tune your marketing plan.
Define your challenges/ objectives ?
As mentioned at the very beginning of this guide I do highlight it again. Before any action please consider what you want to achieve and then prepare the marketing plan according to your goals. Identify your problem and then setup the solution.
Let your goals be SMART ?
Simple, measurable, attainable, realistic and time based. With smart goals you will not be bothered. Setting up too ambitious and unattainable goals will only frustrate you and deteriorate your budget.
Asses your capacities?
Make a check to your resources and prepare technology, people and budget at your goals.
Measure and improve ?
Measure all outputs you will get from your campaigns. Improve what can be improved and change different portion of the budget into most effective channels.
Test, test and test ?
There is no rule of thumb that same marketing channels effective for your rivals will be effective for you, even in the same industry. Yes, inspire yourself but you have to test what fit for your purpose.
Your competition can invest a lot in social media and have perfect results. On the other hand you can invest half of their budget into the pay per click campaigns to have even better result. So, I advise you to test and make your own research for your marketing channels.
Conclusion
Bravo, ? ? you made it till the end. Now you should have very good idea how to setup your marketing plan and let the things run for your success.
You know now that having a good marketing plan is essential when you want to increase your sales, penetrate the market or improve your market share. Most important is to setup your goals correctly and align all the plan according these goals.
Hope you know now how to make a buyer persona analysis as this is your base, first important stepping stone and the whole marketing plan is focusing these personas.
Competitor and situation analysis will improve your decisions about the positioning of your brand, product or service and it will give you a good idea on competitors’ budgets. With your target audience and analysis defined you can know build the media strategy and budget. Please bear in mind your objectives all the time.
At the end you will setup your KPIs and metrics as you can accomplish the given goals.
Well done, I wish you all the luck with your marketing plan you will be preparing and I hope this marketing plan guide will help you to pimp your plan.
Let me know your story about the marketing plan experience, you can write it below in the comments or send me a message.
May the force be with you ?.


