Enterpreneurs with quality and interesting businesses or ideas need a good business plan. Some of the reasons might be efforts to attract an investment/ investor, bank loan, fund or strategic partnership.
Creation of the strategic business plan is not an easy task to do as it may seem. It is more difficult when you are doing it for the first time.
It is quite common mistake that you omit one of the crucial parts of the business plan and you may seem chaotic or poorly prepared in the eye of the investor or strategic partner.
What will you learn in this article?
You will get a detailed grasp what to make a business plan from scratch. This definitive guide will tell you all necessary details you need to have in order to create a business plan for third parties and even for your purposes.
On top of that I prepared templates and downloadable files that will make you much easier to make the business plan. You will learn step by step what is necessary for each chapter of the business plan and what are investors, banks and strategic partners keen on.
I will show you a good outline of a business plan and tell you which part is most important and why.
What content will you find? (Table of contents)
- Developing a business plan – Execution
- Company personnel overview
- Finance and project plan
- Business model
- Financial Statements
- Forecast and break even point (BEP)
- Development timeline, milestones and work-packages
- Risks and opportunities
- Appendix
Files to download


What is a business plan?
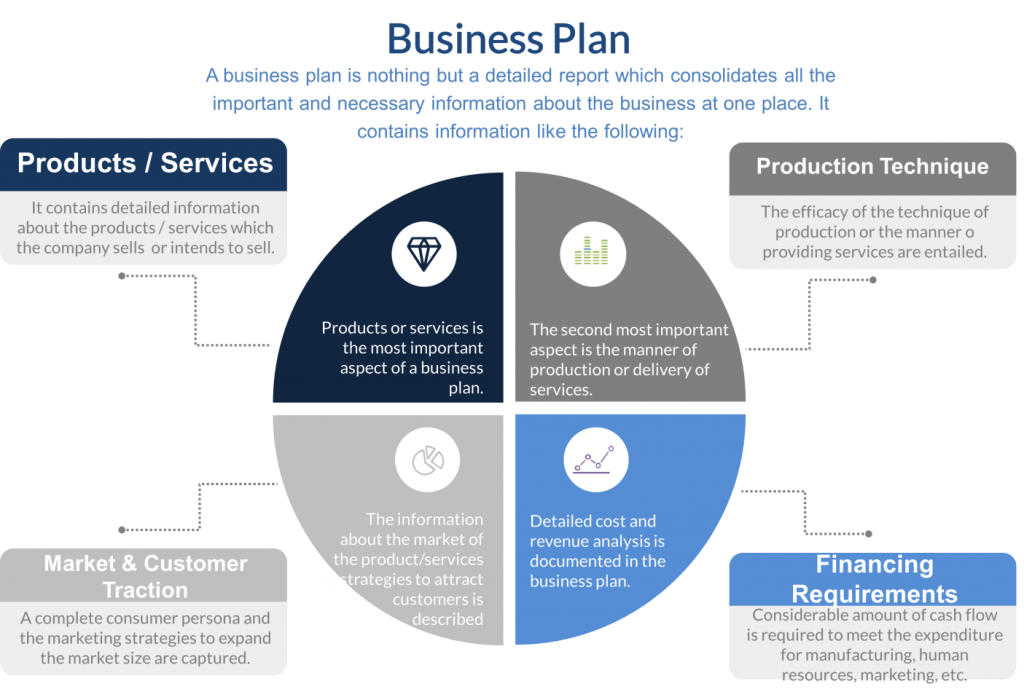
Business plan is a fundamental and strategic document for your business. It is important in cases of investment funding, bank loans, lenders, public funds or other strategic decisions. All necessarry information about the company at one place.
In the nutshell it is a detailed report on a company’s products or services, production techniques, markets and clients, marketing strategy, human resources, organization, requirements in respect of infrastructure and supplies, financing requirements, and sources and uses of funds.
When to write a business plan?
It depends up to the situation. Business plans are written before even the business starts. It is also written during the business when an entrepreneur needs to lend some money or to attract investor or fund.
More detailed answer of this question is going to be very straight forward if you are able to answer the following:
- Need for fast expansion of your business. (National or global markets)
- Need some money to invest into technology and innovations. Product/ service upgrade.
- Need for an investor to enter your company and help you financially.
- Need for a strategic partner to improve your business or product.
- You want any help in form of grants to improve your business/ product/ service.
- Long term decision making.
- Strategic document for partners or board members.
Why to write a business plan?
- The business plan provides you a route for your short and long term goals because of this you are able to identify your Strengths, Weakness, Threats, and Opportunity for your business.
- It also helps you to minimize your loss or maximize your profit.
- Planning the business helps you to optimize your budget and the resources at your disposal.
- It provides a guideline not only to the owner of the business but also to the employees.
For who to write a business plan?
- Investors
- Commercial banks
- Development funds
- European funds
- Multilateral development institutions
- Strategic partners
- Business owners, Board members
- Key employees (C+ level)

1. How to make a business plan
There are some rules and format to present and make a business plan. See the following.
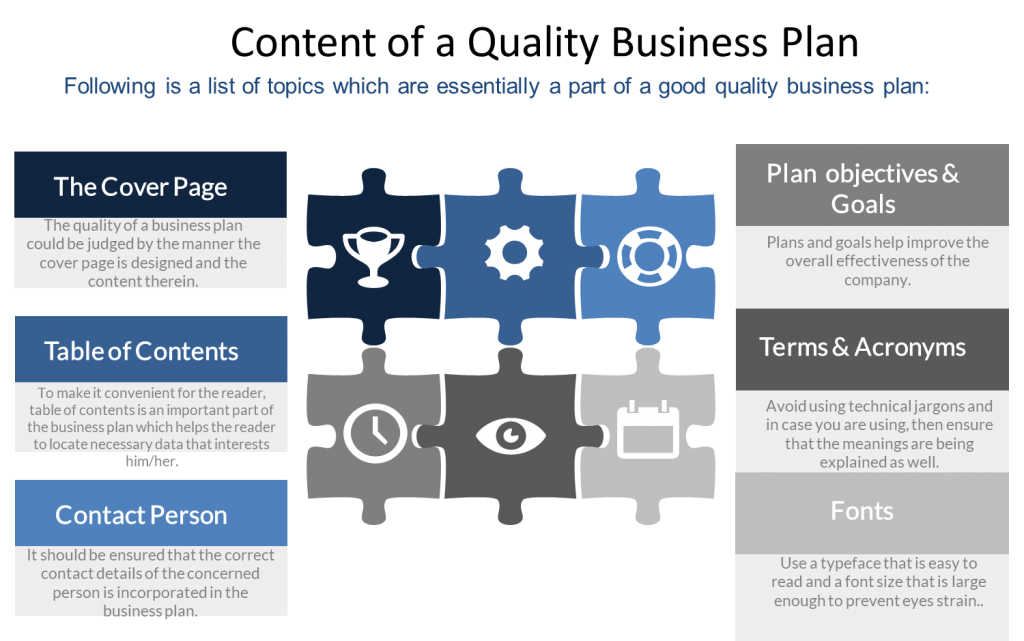
The cover purpose is to tell readers what they are about to read and how to reach the author. Following points are included in the cover page.
Business plan cover should contain:
- The legal name of the business
- Title of your business plan
- The entity’s logo.
- The date of preparation or modification of the document
- The address
- The telephone number
- The e-mail address and website
- Other contact information, if any.
Table of contents provides readers with a quick and easy way to find individual sections in the plan. Be sure to list headings for major sections as well as for important subsections.
Contact person: Be sure to include identifying information for the business and to name the person who should be contacted regarding the plan.
Terms and acronyms: If your business uses specialized terminology or acronyms, use them sparingly and be sure that you define any terms that someone outside your area of expertise would not know.
Executive summary: I recommend one page or maximum two page summary about your business. (Brief history, information about the owners, field of industry, problem on the market and solution of the product, very short product intro). This is very important part as here you can attract the attention of the reader.
Planned objectives & goals: Two important parts of the business plan because Goals establish where you intend to go and tell you when you get there. They help improve your overall effectiveness as a company for example- improve your customer service or the IT services on the other hand. Objectives are the specific steps you and your company need to take to reach each of your goals. They specify what you must do the simple words Goals tell you where you want to go and the objective exactly how to get there .
The total quality of the presentation. Do not go overboard on expensive binders, binding, embossing, etc. According to the form of the plan, more important than its substance can raise doubts among those reading it. But not let it look cheap or sloppy.
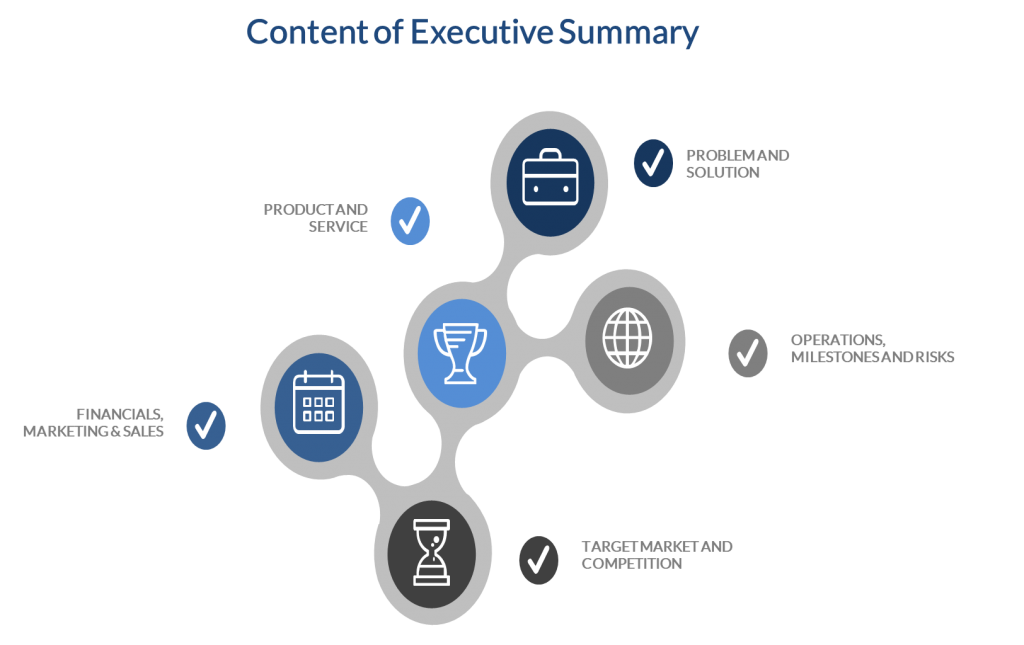
1.1. Writing a Business Plan – Intro to Executive Summary
The executive summary is probably the most significant part of the entire business plan.
It is what most readers will check first. It must be very compelling, up to date and brief with relevant information. Executive summary is some kind of a business plan outline.
Vendors and investors are first to read the executive summary to understand the business plan. They want to see “what, why, how and when answers” to their questions to have a good grasp of your business.
After reading the executive summary investors decide to whether they want to invest in this business or not because they get so many businesses to run in a day they don’t have much time to read all the plans in detail. This is very important part as here you can attract the attention of the reader.
You briefly describe all chapters in points with key message in the executive summary as the reader will exactly know what is going on.
How long should be an executive summary?
It is recommended to have the length of the executive summary from 5% to 10% of total length.
Keep in mind that executive summary is only the business plan outline therefore it ought to contain “key business information (messages)” . Do not overwhelm it. Its main purpose is to briefly inform about the whole business plan and to be granular as possible.
Hint: Investors do not have much time to go deep in detail. Once they are not convinced or impressed in the very beginning they do not even bother to continue in the process.
Executive summary is created at the very end of the business plan. It is important fact that executive summary position is first but it is made after the whole business plan is created.
1.2. Executive Summary
1.2.1. Problem/ Solution
In the executive summary firstly we are talking about the problem which is in the given market therefore what is the problem/ need that customers feel and need to solve. What problem do we solve for your customers?
After describing the problem we have to put the great solution in front of the investors. When writing your Solution you may have various objectives in mind.
The readers you are targeting could also be interested in different aspects. However, the basic objectives of your business plan that you probably need to mention:
- To ensure for yourself the viability of the business you are planning to start (or expand or simply continue the same way)
- To fulfill the need of the customer and to create outstanding solution that help to solve the problem. This solution should be even sustainable and scalable as this elements provide consistent business growh.
- Keep in mind that the executive summary should be very short and you can go into more detail later in the plan.
1.2.2. Intro to Product/ Service
Main questions to be discussed briefly in the executive summary to give the reader a quick overview (of about a half to one page) of your business and the product or the service that we offer are the following:
- What is your company’s type of business? (Production? Services? Trade? What sector?)
- What is the innovation idea (Game changer or strong point of difference)
- What are its product lines and services? What are they used for?
- Where is it located?
- How many employees does it have?
- What is the vision and mission of the business and its objectives?
- When was it formed?
1.2.3. Business model
Briefly describe your business model and revenue streams. Show mainly its viability and potential. Describe your revenue streams.
Do your product/ service has only one revenue stream? Or does it have secondary or tertiary revenue streams?
1.2.4. Operations, milestones & risks
This section of the Executive Summary we are discussing the Operations, Milestones, and risk.
In the operation section talk about the process that takes a set of input resources (material, machinery, information, and customer) which are used to transform something, or are transformed themselves, into outputs of products and service.
Short description of all necessary costs to create your product/ service.
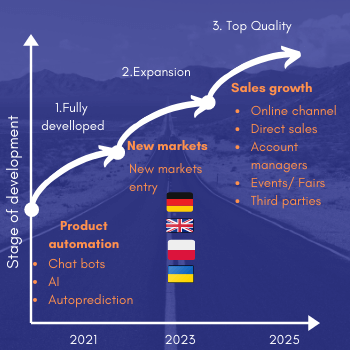
The milestones are one of the most important in the Executive summary. It sets the plan into practical, concrete terms, with real budgets, deadlines, and management responsibilities. It helps you focus as you are writing the business plan, Each action becomes a milestone. This is where a business plan becomes a real plan, with specific and measurable activities, instead of just a document.
You can show your planned timeline in the simple picture.
Investors invest money in the company’s business they must have assessed the risk that the company’s financial results will be lower than forecast.
The risk factors alert the investor to the fact there is always a possibility of a danger he/ she must take into account. Briefly describe main risks and mitigations.
1.2.5. Financials, Marketing & Sales
Financial: marketing and sales are the main objectives of your Executive Summary because it tells investors, lenders or those invested money in your company that How much fund you need for this business plan and for what?
This section should include following:
- What is the total amount of funds you require?
- For which purpose? (Working capital? Purchase of new machinery? Development of new products?
- When do you need the funds? (The first part, the second part, etc.?)
- Are you seeking shareholders’ funds? Loans? Or a combination of both?
- Are your forecasts based on optimistic, realistic or pessimistic assumptions?
- What type of borrowing do you require? (Overdraft? Term loan?) (Facultative)
- How and when do you plan to repay the money? (Mandatory)
- What kind of capital stock is offered to investors? Simply what do you prefer in exchange for the risks and investments? (Preference shares? Common shares? Convertible loans? Other?)
1.2.6. Target market & competition
Target Market refers to the research of potential buying audience for your product. Your target audience is to define your customers/ buyer personas/. Shortly describe your buyer personas (up to 3) in the executive summary. Characterize it within few granular sentences (up to 3-4 sentence per 1 buyer persona.)
Competition is very important to be analyzed. In the executive summary part, define the competition from the highest perspective. (Strong/ Fierce/ Medium or low competition).
Define main competitors and their power. Describe main competitors by few sentences. It is very suspicious if there is no or very low competition in the market. OR you are having a pioneering product/ service.
2. Creating a business plan
2.1. Product/ Service Description
This Section Of the business plan describes our product and service which we serve to customers to fulfill there needs and wants. Product and Service Description included the following:
Product description and history:- In this, we provide product description in detail so if a person is not familiar with our product service they can simply understand how it works, how it works, how long it lasts, what variations and options are available, etc .
Innovation idea: Describe the uniqueness of your product/ service. For instance uniqueness can be ease of use, cost leadership, detailed personalization or other element that competition is missing or having very low competitive advantage.
Investors are very interested in innovative idea it is one of the main points to accept our proposal and invest in our company.
Game changing idea: refers to the idea where we have a strong idea to change the old trend of the market with a new product.
Sometimes we make a business plan for launching a new product in the market for replacement of the old product for example:
– once we use a letter for communication so the letters are replaced by the telephones it makes a big change in the market in this situation we said that it is a game-changing idea.
Product attributes: An effective way to present a particular product or service is to show features/benefits analysis. A feature is a specific product attribute or characteristic. A benefit is an advantage a customer or user will derive from the product or service.
Research and Development: In this section, you should describe any research and development activities that are required before you launch your product. Describe the current stage of your product or service development and give a clear indication of the effort/cost involved and the time required for completion.
Please find attached timeline templates in our files to download slides 5 and 6
Product lifecycle every product has a life cycle. The product life cycle has four parts (some uses five parts) (Development), Introduction, Growth, Maturity, and decline. Understanding this cycle becomes most important as a factor in deciding when it is appropriate to increase advertising, reduce prices, expand to new markets, or redesign packaging.
You can find product lifecycle template in download files here slide 7.
Point of difference (PoD) part tells to investors or board what is the differentiation in the market among the competitors. Usually there can be more points of difference. I would suggest to differentiate in 2-3 points as you can put maximum effort into these points.
Please notice the difference between competitive advantage and point of difference (positioning). Competitive advantage is a distinctive advantage that has a company over its competitors – it can be utilization of its resources or capacities in production.
Simply said, an advantage that allows the company to generate greater sales or margins or even retain more customers.
Point of difference is a product perceived by the customers. Gap in the customer mind. It is a benefit perceived from the product/ service. It can be also history of the business, awareness, product features or brand of the company.
Current state & desired state of development. In this stage, we explain the current stage and desire stage of the product. A gap analysis is the purpose of identifying the differences between your current Stage and Desired Stage.Once it’s complete, you’ll be able to better focus your resources and energy on those identified areas to improve them.
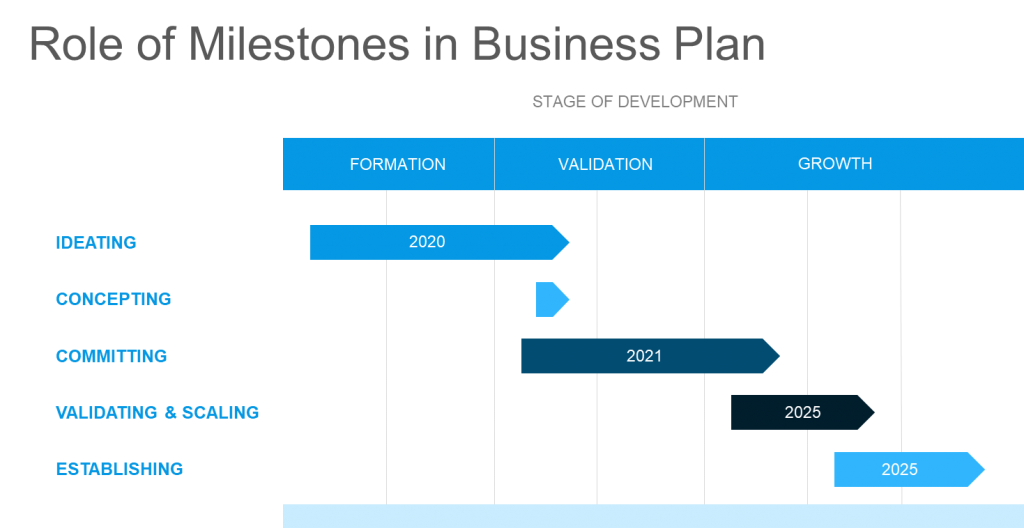
2.2. Activities Taken After the Project – [Facultative]
In case your business plan is the shorter one (25 – 35 pages). I would recommend to include this chapter into it.
In this chapter you simply describe to your audience (investors, banks, funds and other stakeholders) your plans once your product/ service will be fully developed or once you reach desired state.
It is worth to mention few after project activities to show the audience that your are serious about your plan. Mentioned after project activities:
- Best in class – Reaching a high technology state of development in your class. Technology leader in the market.
- Sustainable development – Company development and its steps in future. This mean to secure succession planning, know-how transfer and raising own experts.
- Organization growth – Expansion to new markets force the growth of the company. Revenue growth means new processes implementation. It is important to envisage the size of the company and the management.
- New markets – External view to organization. New markets opening and horizontal company growth.
3. Opportunity
The aim of this section is to convince investors and lenders that there is an opportunity in the market for your product or the service :
- You have a thorough understanding of the market and its size. (See picture below )
- Market demand forecast and growth (CAGR).
- There is a demand for your product or service.
- Your company is sufficiently competitive to get a good share of the market.
3.1. Target Market
In this section of business plan we introduce our market to the investors or the lenders. Using a description of your target audience. Here you should summarize particulars regarding the current size of your target market and its growth potential in the short, medium and long term.
You also provides the any growth estimates with factors such as industry trends, new technological developments, socio-economic trends, government policy, population shifts and changing customer needs.
Example of the PEST analysis for the segment of utility – gas stations.
You can find template for PEST analysis in documents to download slide 10.
Market definition (General approach):
- Market ecosystem
- Market characteristics
- PEST analysis
- Trends and threats in the market
Market definition (Detailed approach):
- Market size and growth
- Market forecast (3-5 years)
- Market conditions
- 5 force analysis (Porter analysis : Intensity of rivalry, negotiation power of suppliers and buyers, threat of substitutes, threat of new entrants.)
Willingness to pay
In this small section I recommend to descibe the reason why should customer pay for the product/ service. You can describe this willingness through the benefits for the customer – Unique Selling Proposition (USP)
For instance it can be:
- Ease of use
- Money and time saving (in %)
- Innovation and technology level
- Other attributes perceived by the client (brand etc.)
3.2. Target Audience
In this section outline the existing and identified target audience groups or major single customer (key accounts) because indirectly we are mainly produce and good or service for the consumer so its important to identify them correctly. There are some points which helps you to understand your potential buying audience.
- Who they are?
- Where are they located?
- What & why do they buy? How much is their monthly spending?
- When and under what circumstances do they buy?
- What types of concerns do they have?
- What are their expectations concerning price, quality and service?
After answering all the questions you surely get your potential buying audience and make them customers. In this section we include the buyer persona pain points and solutions of the customers.
You can find buyer persona template (B2C, B2B) in files to download, slide 8 and 9.
3.3. Competition & Competitive Offerings
In this Section you should provide the detailed competition overview of the market. It is important to describe your direct and indirect competition.
Your competition should consist of several main elements:
- Short competitor description
- Financial information
- Business model
- Point of difference
- Segment of operation
- Service offerings with pricing

Additional templates you can add into your business plan structure. Supply chain – slide 1. Value chain – slide 2. Competitive advantage – slide 3.
3.4. Scalability
Do you want to be attractive for new investors or funds? Do you want to expand to new markets at lowest barriers? The answer is business scalability which simply means to scale (grow, expand) your business model very simple into other markets.
Scalability definition: Scalability is a characteristic of a system, model or, function that describes its capability to cope and perform well under an increased or expanding workload or scope.
Simply said scalability is an ability of a product/ service to be applicable for other markets with any minimal adjustments. Let’s take a look for an example such as SaaS online service.
If you are providing any SaaS service online you can simply scale it by language mutations and open new markets quite easily after adjusting and following market rules and legislation of each opening market (country).
There are several points/ advantages that your product/ service will profit from scalability:
- Total expenses lowering: Once you open new markets it is usual that costs will decrease as you have almost same development cost for the service itself and margin will grow.
- Customization and deployment is easier.
- Lowering customer acquisition costs (CAC).
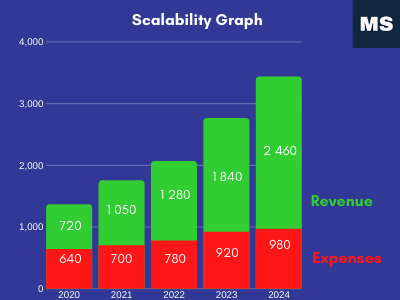
Ability to scale-up your business potential is very crucial for each investor or fund. This parameter express the quality of business idea and its potential.

